(WASHINGTON) — A deteriorated bollard led to a mobile offshore drilling unit breaking away and striking a cargo vessel in Pascagoula, Miss., last year, the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) has determined. The breakaway resulted in nearly $5 million in damage.
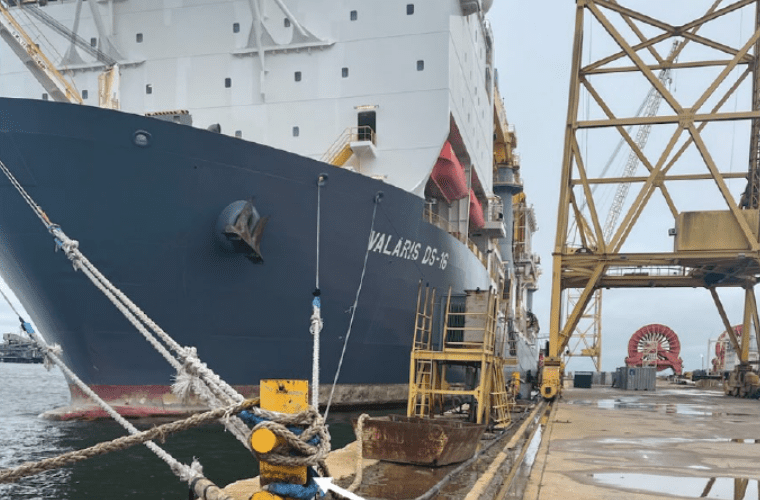
On March 12, 2022, the mobile offshore drilling unit Valardis DS-16 was at the ST Engineering Halter Marine and Offshore Shipyard (STEHMO) when it broke away from the dock during the passage of a cold front, drifted across the Bayou Casotte Channel and struck the bulk cargo vessel Akti. No injuries or pollution were reported.
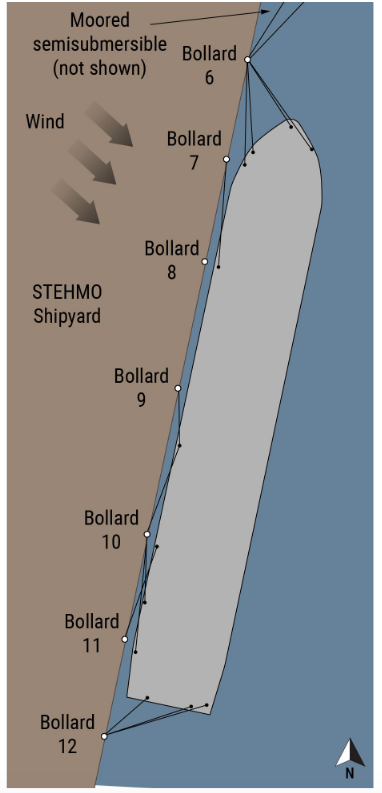
Valardis DS-16’s mooring lines were placed on six bollards on the pier at STEHMO. During winds of 30 to 40 knots, one of the bollards broke free at its base and was pulled off the pier into the water. The snapped bollard secured Valardis DS-16’s four bow lines and a semisubmersible rig’s two stern lines.
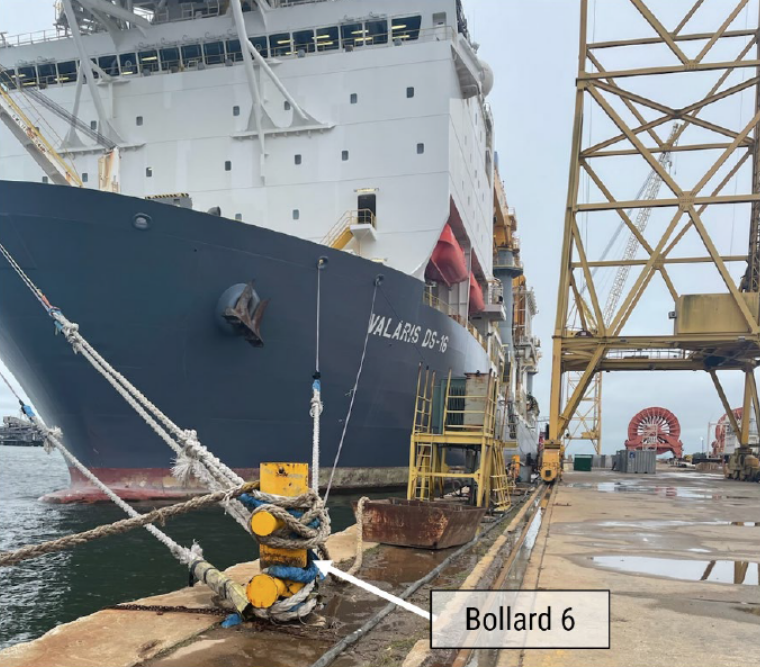

Ultrasonic thickness tests performed after the breakaway indicated there was deteriorated steel at the lower portion of several bollards. Several bollards also showed signs of external corrosion and wastage. In addition, all of the bollards used by Valardis DS-16 were modified from the original 1997 design, and vertical components were added to each of the bollards to accommodate more lines.
The NTSB determined the probable cause of the breakaway and subsequent impact with the cargo vessel was the failure of one of the shipyard’s mooring bollards — which had been modified to increase its height to accommodate more lines — used to secure Valardis DS-16’s bow mooring lines to a pier.
STEHMO has replaced 10 of the 14 bollards on the pier, with plans to replace an 11th bollard by the end of March 2023. Shipyard managers have begun evaluating the safe working load of the new bollards and are scheduling a pull test using a tugboat.
“As a result of continuing increases in vessel size and sail area, bollards that were previously sufficient may not have adequate capacity to moor larger vessels,” the NTSB report said. “There are currently no U.S. Coast Guard or Occupational Safety and Health Administration regulatory requirements for facilities to inspect and verify loading capacities of bollards at shoreside facilities. Bollards and associated pierside mooring equipment are vital equipment that must be capable of withstanding the tremendous forces that large vessels exert on them. Due to their exposure to seawater, bollards and associated pierside mooring equipment are at high risk for corrosion, which can significantly affect service life. The Coast Guard has recommended that facility owners and operators develop a routine inspection program for bollards and other mooring equipment.”
Marine Investigation Report 23-05 is available here.
– National Transportation Safety Board

